|
The Council initiated the Karnataka Natural Resources Data
Management System (NRDMS) program in 1992 and since then
established District NRDMS Centers in all the State with
active support and funding from Department of Science &
Technology (DST) Government of India and Government of
Karnataka. NRDMS program is a multi-disciplinary and
multi-institutional program of the Council aimed at developing
methodologies for building and promoting the use of spatial
data management and analysis technologies in local area
planning. The initial approach of planning based on macro
level assessment of resources did not yield the desired
results. The introduction of the concept of spatial planning
to micro-levels by the Planning commission paved the way for
evolution of NRDMS program. The vision of the NRDMS program
during its inception was to provide S&T inputs for
operationalising the concept of decentralized planning of the
country by developing computer compatible spatial databases on
natural resources, socio and agro-economic parameters to
further the concept of area specific decentralized planning.
Resource knowledge and resource inventory is crucial to
spatial planning. At the core of this concept lies an
integrated approach to planning in contrast to the sectoral
method. This requires a detailed knowledge of the
interrelations and interdependencies between various sectors
to resolve often-conflicting demands. This leads to a
requirement for appropriate data management and analyzing
tools and techniques and a large matrix of sectoral data, in
digital format, on natural resources, demography,
socio-economy etc. and integrating them to generate
appropriate information/applications required for plan
preparation.
The district NRDMS centers since inception have created an
exhaustive database of natural resources, socio-economic
parameters, infrastructure etc. The NRDMS centres are
providing analyzed/value added information to planners and
administrators besides developing applications using
geo-spatial technologies suitable for local level planning.
The NRDMS centers are providing need-based information to
users such as elected bodies, district administration and
planners through maps, charts, tables, and reports etc., on
spatial and non-spatial data.
Enabling people, communities and institutions of local-self
governance with requisite databases and S & T tools for
informed participation in local self-governance.
The corresponding goals of the Programme to realize the above
vision could be the following:
To strengthen the S&T inputs in developing tools and
techniques for integrated resource and infrastructure capacity
building at various levels for planning and implementation in
a spatio-temporal context in a multi-level framework below the
district.
Go
Top
Genesis of NRDMS
The balanced
regional development and effective implementation of the basic
needs of our society depends on the planning process which was
initially the sectoral approach confined to the central level.
This accentuated the inter and intra-regional disparities in
the development and hence there was necessity to decentralize
the planning process to smaller area units. During the VIII
five-year plan a special emphasis was rightly given to the
concept of decentralized planning. While adopting the seventy
third and seventy fourth constitutional amendment acts (1992),
a set of specific items covering various sectors viz., land,
water, agro-economy etc., were identified. Concerned agencies
were required to prepare and implement integrated development
schemes. This growing urge for decentralizing the process and
practice of planning prompted to take a fresh look at methods
of data management.
In line with the
above policy, the Natural Resources Data Management System
(NRDMS) project was launched by the Department of Science and
Technology, Government of India.
The basic
imperative behind evolving NRDMS are:
1. Large
diversity of spatial data.
2. Many types of data are used for more than one purpose by
more than one user.
3. Utility of data set may be greatly enhanced by merging or
linking it with other data sets.
4. Reliability / consistency can be enhanced by correlating
different parameters.
5. Many organisations are involved in data collection and
updating.
6. Need for standardisation / compatibility of procedures of
data collection and adoption.
7. Need to improve the utilisation of data for decision
making.
The overall
objective of the NRDMS is to increase the efficiency of
utilization of resources through the application of scientific
management principles and Geographical Information System
[GIS] technology.
Go
Top
-
Large diversity of spatial data.
-
Many types of data are used for more than one purpose by
more than one user.
-
Utility of data set may be greatly enhanced by merging or
linking it with other data sets.
-
Reliability / consistency can be enhanced by correlating
different parameters.
-
Many organisations are involved in data collection and
updating.
-
Need for standardisation / compatibility of procedures of
data collection and adoption.
-
Need to improve the utilisation of data for decision making.
-
To
develop, demonstrate methods/techniques and tools for
operationalsing the concept of "Decentralized (Local level)
Planning" using geospatial technologies.
-
To
provide value added information for district level planning
using geospatial database.
-
Development of integrated digital database for generating
-
Resource profiles
-
Query-based information
-
Static and dynamic outputs based on Spatial Decision
Support System (SDSS).
-
Interaction through workshops with line department officials
and stakeholders at multi-level to assess their information
needs in implementing the schemes and capacity building.
-
To develop local specific applications using GIS tools.
-
To create awareness among end-users about the utility of GIS
technologies by conducting regular training programs and
workshops.
-
Documentation and dissemination.
-
To establish district NRDMS centers in all the districts to
develop database and applications that are relevant to
planning and administration.
Go
Top
 View
/ Download Karnataka NRDMS Brochure View
/ Download Karnataka NRDMS Brochure
NRDMS
Methodology
NRDMS programme
aims to analyze the evolution of methodologies and techniques
for formulating development strategies. In a scenario of large
diversity of data sets, data users and data generating
agencies, the programme aims at developing and demonstrating
the use of spatial decision support tools for integrated
planning and management of resources at the local level. The
NRDMS programme uses both maps and textual data collected from
various data generating agencies and remote sensing sources.
Maps are digitized and stored on a computer as a series of
thematic data layers. Depending on the real unit of planning,
maps on 1:250,000, 1:50,000 and cadastral scales are utilized.
Data on natural resources, demography, agro & socio-economy
and infrastructural facilities for a district form the core
database. Those pertaining to specific problems of an area
constitute the sectoral database. Textual data obtained from
secondary sources are normally stored with village as a unit.
Data gaps are filled in by limited primary surveys. Various
decision support systems \ modules built into the system help
process the data and generate alternative scenarios for making
optimal planning decisions. Outputs in the form of thematic
maps, tables and reports based on spatial analysis are
obtained from the database as per the user requirements.
The
diagram below indicates broadly the methodology adopted in the NRDMS project.
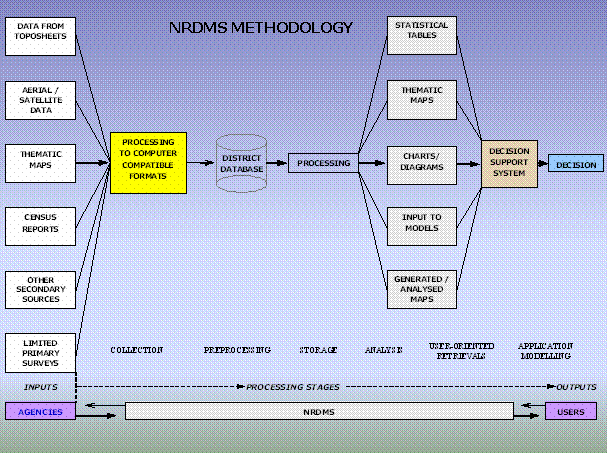
Go
Top
Geographical
Information System [GIS]
A geographic information system (GIS), captures, stores,
analyzes, manages, and presents data that is linked to
location. Technically, GIS is geographic information systems
which includes mapping software and its application with
remote sensing, land surveying, aerial photography,
geo-positioning system, mathematics, photogrammetry,
geography, and tools that can be implemented with GIS
software. GIS applications are tools that allow users to
create interactive queries (user created searches), analyze
spatial
information, edit data, maps, and present the results of all
these operations.
GIS have taken advantage of rapid developments in Information
technology over the past several decades to address the
spatial challenges of storing and analyzing spatial data. GIS
belongs to the class of computer systems that require the
building of large databases before they actually become
useful. Actually, the use of a GIS requires that large spatial
database be created, appropriate hardware / software be
procured and installed, applications be developed, installed,
integrated and tested before users can use the GIS and realize
the benefit.
The role of a GIS in a government setup is more than simply
automating a few obvious tasks for the sake of efficiency. A
local government or zilla panchayath should view the GIS
project as an opportunity to introduce fundamental change into
the way its business is conducted. Just as MIS / EIS in
corporate business world, the adoption of GIS effectively
reorganises the data and information that the government
collects, maintains and uses to conduct its affairs. This will
lead to major changes in the institution both effectiveness
and efficiency of operations. NRDMS uses corporate database
concept to integrate GIS data for all units of Zilla
Panchayath participating in a co-operative GIS program.
Establishing the corporate database is much more a question of
policy, management co-operation and co-ordination.
An
effective corporate database does require co-operation on the
part of all users, both for collection and entry of data in
the database and in developing applications in a shared data
context. This may result in some individual applications or
uses being less efficient, however the overall benefits to the
organization can easily out weigh these inefficiencies.
Greater emphasis must be placed on maintaining a high quality
of data and services to users.
Go
Top
|








